1、HDF5介绍
HDF 是用于存储和分发科学数据的一种自我描述、多对象文件格式。HDF 是由美国国家超级计算应用中心(NCSA)创建的,以满足不同群体的科学家在不同工程项目领域之需要。HDF 可以表示出科学数据存储和分布的许多必要条件。HDF 被设计为:
- 自述性:对于一个HDF 文件里的每一个数据对象,有关于该数据的综合信息(元数据)。在没有任何外部信息的情况下,HDF 允许应用程序解释HDF文件的结构和内容。
- 通用性:许多数据类型都可以被嵌入在一个HDF文件里。例如,通过使用合适的HDF 数据结构,符号、数字和图形数据可以同时存储在一个HDF 文件里。
- 灵活性:HDF允许用户把相关的数据对象组合在一起,放到一个分层结构中,向数据对象添加描述和标签。它还允许用户把科学数据放到多个HDF 文件里。
- 扩展性:HDF极易容纳将来新增加的数据模式,容易与其他标准格式兼容。
- 跨平台性:HDF 是一个与平台无关的文件格式。HDF 文件无需任何转换就可以在不同平台上使用。
(官方介绍:https://support.hdfgroup.org/HDF5/whatishdf5.html)
2、HDF5的文件组织
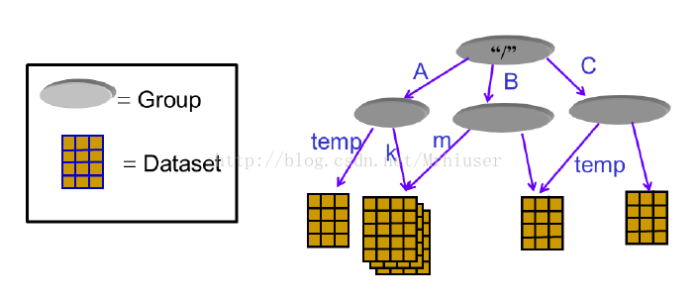
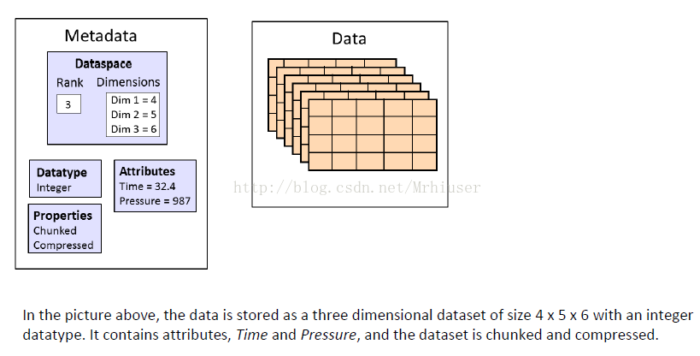
一个HDF5文件就是一个由两种基本数据对象(groups and datasets)存放多种科学数据的容器:
- HDF5 group: 包含0个或多个HDF5对象以及支持元数据(metadata)的一个群组结构
- HDF5 dataset: 数据元素的一个多维数组以及支持元数据(metadata)
3、HDF5软件下载
https://support.hdfgroup.org/HDF5/release/obtain518.html
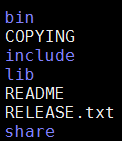
4、目录结构
下载后解压
- bin目录是已经编译的好的可执行文件。例如:bin目录下的h5dump可以查看h5文件。
- include目录是编写代码是需要包含的头文件。
- lib目录是编译代码时需要连接的库。
- share目录中是example。
5、 example code
- #include<stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include "H5Cpp.h" //包含HDF5需要的头文件
- #ifndef H5_NO_NAMESPACE
- using namespace H5;
- #ifndef H5_NO_STD
- using std::cout;
- using std::endl;
- #endif // H5_NO_STD
- #endif
- const H5std_string FILE_NAME("h5_test.h5");//定义要创建的文件名字
- const int RANK = 2; //定义数组的维度
- const int M = 3;
- const int N = 4;
- int main(void)
- {
- const H5std_string GROUP_NAME("MyGroup");//定义要创建group的名字
- const H5std_string DATASET_NAME("MyData");//定义要创建dataset的名字
- const H5std_string ATTR_NAME( "MyAttribute" );//定义要创建数据集属性的名字
- //准备要存储的数据
- float *data = (float*)malloc(M*N*sizeof(float));
- float *tmp=NULL;
- for(int i =0; i<M; ++i){
- for(int j =0; j<N; ++j){
- tmp = data + i*N +j;
- *tmp = 1.3;
- }
- }
- try
- {
- // Turn off the auto-printing when failure occurs so that we can
- // handle the errors appropriately
- Exception::dontPrint();
- //创建文件
- H5File file(FILE_NAME, H5F_ACC_TRUNC);
- //创建 group
- Group group(file.createGroup(GROUP_NAME));
- //创建数据空间
- hsize_t dims[RANK]; // dataset dimensions
- dims[0] = M;
- dims[1] = N;
- DataSpace *dataspace = new DataSpace (RANK, dims);
- //创建数据集
- DataSet *dataset = new DataSet (group.createDataSet(DATASET_NAME, PredType::NATIVE_FLOAT, *dataspace));
- //将准备好的数据,写到数据集中。
- dataset->write(data, PredType::NATIVE_FLOAT);
- // 创建数据集属性空间.
- int attr_data[2] = { 100, 200};
- hsize_t attr_dims[1] = { 2 };
- DataSpace attr_dataspace = DataSpace (1,attr_dims );
- // 创建数据集的属性.
- Attribute attribute = dataset->createAttribute( ATTR_NAME, PredType::STD_I32BE, attr_dataspace);
- // 写属性.
- attribute.write( PredType::NATIVE_INT, attr_data);
- // 关闭数据空间、数据集、group对象.
- delete dataspace;
- delete dataset;
- group.close();
- }
- // catch failure caused by the H5File operations
- catch(FileIException error)
- {
- error.printError();
- return -1;
- }
- // catch failure caused by the DataSpace operations
- catch(DataSpaceIException error)
- {
- error.printError();
- return -1;
- }
- // catch failure caused by the Group operations
- catch(GroupIException error)
- {
- error.printError();
- return -1;
- }
- // catch failure caused by the DataSet operations
- catch(DataSetIException error)
- {
- error.printError();
- return -1;
- }
- return 0;
- }
6、编译
- g++ example.cpp -o example -I./include -L./lib -lhdf5_cpp
7、执行
- ./example
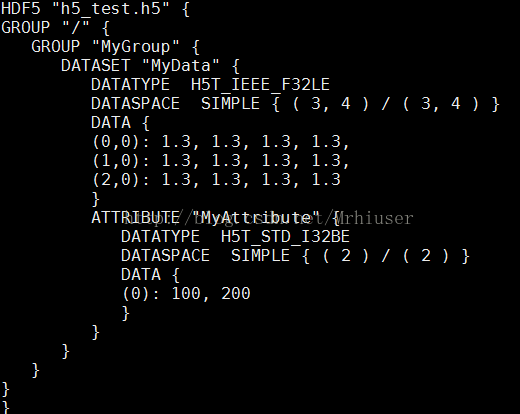
生成一个 h5_test.h5文件
8、查看
可是使用bin目录的h5dump 查看 命令