概述
BEDTools是可用于genomic features的比较,相关操作及进行注释的工具。而genomic features通常使用Browser Extensible Data (BED) 或者 General Feature Format (GFF)文件表示,用UCSC Genome Browser进行可视化比较。
与BEDTools使用相关的基本概念
已有的一些genome features信息一般由BED格式或者GFF格式进行存储。
genome features: 功能元素(gene), 遗传多态性 (SNPs, INDELs, or structural variants), 已经由测序或者其他方法得到的注释信息,也可以是自定义的一些特征信息。
Overlapping/intersecting features: 两个genome features的区域至少有一个bp的共同片段。
BED和GFF文件的一个差异
BED文件中起始坐标为0,结束坐标至少是1,; GFF中起始坐标是1而结束坐标至少是1。
相关格式
BED format
BEDTools主要使用BED格式的前三列,BED可以最多有12列。BED格式的常用列描述如下:
- chrom: 染色体信息, 如chr1, III, myCHrom, contig1112.23, 必须有
- start: genome feature的起始位点,从0开始, 必须有
- end: genome feature的终止位点,至少为1, 必须有
- score: 可以是p值等等一些可以刻量化的数值信息
- strands: 正反链信息
GFF format
seqname - name of the chromosome or scaffold; chromosome names can be given with or without the ‘chr’ prefix. Important note: the seqname must be one used within Ensembl, i.e. a standard chromosome name or an Ensembl identifier such as a scaffold ID, without any additional content such as species or assembly. See the example GFF output below.
source - name of the program that generated this feature, or the data source (database or project name)
feature - feature type name, e.g. Gene, Variation, Similarity
start - Start position of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1.end - End position of the feature, with sequence numbering starting at 1.
score - A floating point value.strand - defined as + (forward) or - (reverse).
frame - One of ‘0’, ‘1’ or ‘2’. ‘0’ indicates that the first base of the feature is the first base of a codon, ‘1’ that the second base is the first base of a codon, and so on..
attribute - A semicolon-separated list of tag-value pairs, providing additional information about each feature.
See more from http://www.ensembl.org/info/website/upload/gff.html
genome files
BEDTools中的一些工具(genomeCoverageBed, complementBed, slopBed)需要物种的染色体大小的信息,genome file一般就是每行都是tab隔开,两列,一列为染色体的名字,第二列为这个染色体的大小。一般常用物种的genome file在BEDTools安装目录的/genome里面。
自定义基因组genome files文件生成方法见我的另一篇博文:批量求fasta格式序列长度。
BEDTools使用总结
intersect/intersectBed:计算 Overlaps
- bedtools intersect -a A.bed -b B.bed -wa -wb
用来求两个BED或者BAM文件中的overlap,overlap可以进行自定义是整个genome features的overlap还是局部。
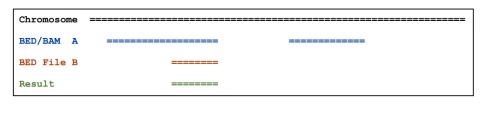
加-wa参数可以报告出原始的在A文件中的feature, 如下图
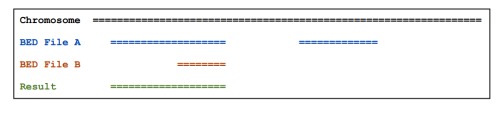
加-wb参数可以报告出原始的在B文件中的feature, 加-c参数可以报告出两个文件中的overlap的feature的数量。
当用bedtools intersect 处理大文件时比较耗内存,有效的方法是对A和B文件按照染色体名字(chromosome)和位置(position)排序(sort -k1,1 -k2,2n),然后用-sorted参数重新intersect。
- bedtools intersect -a A-sorted.bed -b B-sorted.bed --sorted
其他参数:
-wo 返回overlap碱基数
- $bedtools intersect -a A.bed -b B.bed -wo
- chr1 0 15 a chr1 0 4 x 4
- chr1 0 15 a chr1 9 15 z 6
- chr1 25 29 b chr1 18 28 y 3
- chr1 18 18 c chr1 18 28 y 1
- chr1 10 14 d chr1 9 15 z 4
- chr1 20 23 e chr1 18 28 y 3
-v 返回非overlap区间
-s 相同链上的feature
-c 两个文件中的overlap的feature的数量
complement:返回基因组非覆盖区
- bedtools complement -i <BED/GFF/VCF> -g <genome files>
Slop:增加特征区间大小
要求:单个输入bed文件(-i指定)和genome files
- cat ranges-qry.bed
- chr1 0 15 a
- chr1 25 29 b
- chr1 18 18 c
- chr1 10 14 d
- chr1 20 23 e
- chr1 6 7 f
- bedtools slop -i ranges-qry.bed -g genome.txt -b 4
- chr1 0 19 a
- chr1 21 33 b
- chr1 14 22 c
- chr1 6 18 d
- chr1 16 27 e
- chr1 2 11 f
- #-b 4 :两端同时缩短4个碱基
-l 3 -r 5:增加左3右5
flank:提取特定区域(启动子区)
要求:基因组GTF文件(-i指定)和genome files
- bedtools flank -i mm_GRCm38.75_protein_coding_genes.gtf \
- -g Mus_musculus.GRCm38_genome.txt \
- -l 3000 -r 0 > mm_GRCm38_3kb_promoters.gtf
- cut -f1,4,5,7 mm_GRCm38_3kb_promoters.gtf | head -n 3
- 1 3671499 3674498 -
- 1 4360315 4363314 -
- 1 4496414 4499413 -
getfasta:提取序列
要求:基因组fasta文件(-fi指定)和提取区间GTF文件(-bed指定)
- bedtools getfasta -fi Mus_musculus.GRCm38.75.dna_rm.toplevel_chr1.fa \
- -bed mm_GRCm38_3kb_promoters.gtf -fo mm_GRCm38_3kb_promoters.fasta
-tab Report extract sequences in a tab-delimited format instead of in FASTA format.
提取序列之samtools(速度较快)
- #首先建立fai索引文件(第一列为染色体名字,第二列为序列碱基数)
- samtools faidx Mus_musculus.GRCm38.75.dna.chromosome.8.fa
- #序列提取,多提取区间空格隔开
- samtools faidx Mus_musculus.GRCm38.75.dna.chromosome.8.fa \
- 8:123407082-123410744 8:123518835-123536649
- >8:123407082-123410744
- GAGAAAAGCTCCCTTCTTCTCCAGAGTCCCGTCTACCCTGGCTTGGCGAGGGAAAGGAAC
- CAGACATATATCAGAGGCAAGTAACCAAGAAGTCTGGAGGTGTTGAGTTTAGGCATGTCT
- [...]
- >8:123518835-123536649
- TCTCGCGAGGATTTGAGAACCAGCACGGGATCTAGTCGGAGTTGCCAGGAGACCGCGCAG
- CCTCCTCTGACCAGCGCCCATCCCGGATTAGTGGAAGTGCTGGACTGCTGGCACCATGGT
- [...]
nuc: 计算GC含量即各碱基数
- bedtools nuc -fi hg19.fa -bed CDS.bed
输出结果解释:在原bed文件每行结尾增加以下几列
- Output format:
- The following information will be reported after each BED entry:
- 1) %AT content
- 2) %GC content
- 3) Number of As observed
- 4) Number of Cs observed
- 5) Number of Gs observed
- 6) Number of Ts observed
- 7) Number of Ns observed
- 8) Number of other bases observed
- 9) The length of the explored sequence/interval.
- 10) The seq. extracted from the FASTA file. (opt., if -seq is used)
- 11) The number of times a user's pattern was observed.
- (opt., if -pattern is used.)
genomecov:染色体和全基因组覆盖度计算
要求:单个输入bed文件(-i指定)和genome files;如果输入为bam(-ibam指定)文件,则不需要genome files。
- cat ranges-cov-sorted.bed
- chr1 4 9
- chr1 1 6
- chr1 8 19
- chr1 25 30
- chr2 0 20
- $ cat cov.txt
- chr1 30
- chr2 20
- bedtools genomecov -i ranges-cov-sorted.bed -g cov.txt
- chr1 0 7 30 0.233333 1
- chr1 1 20 30 0.666667
- chr1 2 3 30 0.1
- chr2 1 20 20 1 2
- genome 0 7 50 0.14 3
- genome 1 40 50 0.8
- genome 2 3 50 0.06
- #name 覆盖次数 覆盖碱基数 总碱基数 覆盖度
- #同时计算单染色体和全基因组覆盖度
- ranges-cov.bed文件需提前排序sort -k1,1 ranges-cov.bed > ranges-cov-sorted.bed
- -bg参数可得到每个碱基的覆盖度。
coverage:计算染色体给定区间覆盖度
- $ cat A.bed
- chr1 0 100
- chr1 100 200
- chr2 0 100
- $ cat B.bed
- chr1 10 20
- chr1 20 30
- chr1 30 40
- chr1 100 200
- $ bedtools coverage -a A.bed -b B.bed
- chr1 0 100 3 30 100 0.3000000
- chr1 100 200 1 100 100 1.0000000
- chr2 0 100 0 0 100 0.0000000