这一篇会在之前的基础上开始在circos绘制基因密度信息。为了保证一致性,可以新建如下几个文件
circos.conf:
- karyotype = karyotype.tair10.txt
- chromosomes_color = chr1=rdylbu-11-div-1,chr2=rdylbu-11-div-3,chr3=rdylbu-11-div-5,chr4=rdylbu-11-div-7,chr5=rdylbu-11-div-9
- chromosomes_units = 1000000
- <<include ticks.conf>>
- <ideogram>
- <spacing>
- default = 0.005r
- </spacing>
- radius = 0.90r
- thickness = 20p
- fill = yes
- stroke_color = dgrey
- stroke_thickness = 2p
- show_label = yes #展示label
- label_font = default # 字体
- label_radius = dims(ideogram,radius) + 0.05r #位置
- label_size = 16 # 字体大小
- label_parallel = yes # 是否平行
- label_format = eval(sprintf("%s",var(chr))) # 格式
- </ideogram>
- <image>
- dir* = . # 输出文件夹
- radius* = 500p # 图片半径
- svg* = no # 是否输出svg
- <<include etc/image.conf>>
- </image>
- <<include etc/colors_fonts_patterns.conf>>
- <<include etc/housekeeping.conf>>
karyotype.tair10.txt
- chr - chr1 chr1 0 30427617 chr1
- chr - chr2 chr2 0 19698289 chr2
- chr - chr3 chr3 0 23459830 chr3
- chr - chr4 chr4 0 18585056 chr4
- chr - chr5 chr5 0 26975502 chr5
ticks.conf
- show_ticks = yes
- show_tick_labels = yes
- <ticks>
- radius = 1r
- color = black
- thickness = 2p
- multiplier = 1e-6
- format = %d
- <tick>
- spacing = 1u
- size = 5p
- </tick>
- <tick>
- thickness = 4p
- spacing = 5u
- size = 10p
- show_label = yes
- label_size = 10p
- label_offset = 10p
- format = %d
- </tick>
- </ticks>
在开始之前,请确保已经安装了bedtools,如果没有的话,用conda安装
- # 安装bedtools
- conda install -c bioconda bedtools
数据格式
为了能够在circos绘制基因密度信息,需要先知道circos要求的输入数据格式是什么。
对于折线图(line),散点图(scatter),柱状图(histogram)和热图(heatmap),Circos要求的数据输入格式相同,也就是chr start end value [options], 如果熟悉BED格式定义的话,你就会发现除了可选(options)外,Circos要求的格式就是4列的BED。
对于可选列,可以和circos.conf里的搭配使用,属于比较高级的用法。
数据预处理
为了能够获得所需的基因密度信息,我们需要下载拟南芥的GFF文件。
- # download
- wget ftp://ftp.ensemblgenomes.org/pub/plants/release-44/gff3/arabidopsis_thaliana/Arabidopsis_thaliana.TAIR10.44.gff3.gz
提取基因的位置信息
zgrep '[[:blank:]]gene[[:blank:]]' Arabidopsis_thaliana.TAIR10.44.gff3.gz | cut -f 1,4,5 | awk '{print "chr"$1"t"$2"t"$3}' > genes.bed
接着用bedtools以500kb为滑窗,沿染色体创建窗口
cut -d ' ' -f 3,6 karyotype.tair10.txt | tr ' ' 't' > tair10.genomebedtools makewindows -g tair10.genome -w 500000 > tair10.windows
最后统计信息
bedtools coverage -a tair10.windows -b genes.bed | cut -f 1-4 > genes_num.txt
展示信息
我们可以先用最少的参数,同时展示不同的图形。
- ...
- <plots>
- <plot>
- type = line
- thickness = 2
- max_gap = 1u
- file = genes_num.txt
- color = redv
- r0 = 0.51r
- r1 = 0.60r
- </plot>
- <plot>
- type = heatmap
- file = genes_num.txt
- color = spectral-5-div
- r1 = 0.70r
- r0 = 0.61r
- </plot>
- <plot>
- type = scatter
- fill_color = grey
- stroke_color = black
- glyph = circle
- glyph_size = 10
- file = genes_num.txt
- r1 = 0.80r
- r0 = 0.71r
- </plot>
- <plot>
- type = histogram
- file = genes_num.txt
- r1 = 0.89r
- r0 = 0.81r
- </plot>
- </plots>
- ...
运行之后,效果如下
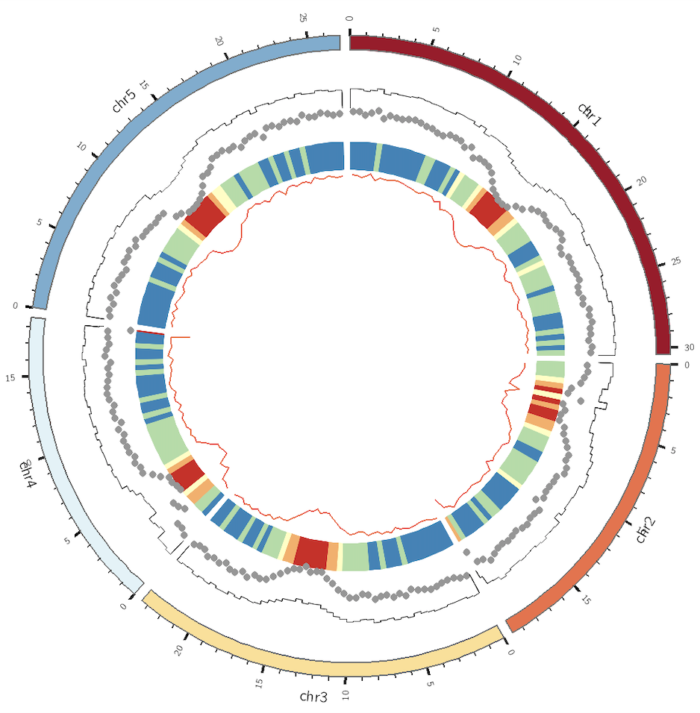
这张图展示了巨大的进步空间,至少可以从如下几个角度进行调整,
- 柱状图有点丑,需要填充颜色
- 热图的颜色不符合直觉,基因数越少反而颜色越深
- 散点图的点太大
- 有些图形可能需要加上背景色。
- 对于一些过大的数值,最好用一种颜色表示。
当知道自己的目标后,后续的事情就是找对应参数和调整参数. 部分我用来调整参数如下
show- 是否展示该图形type- 展示的图形类型file- 输入的数据文件所在路径min/max- 数据范围r0/r1- 内径和外径,在圈图中的位置glyph- 对于散点图而言,还可以选择符号的类型,是circle, rectangle, 还是 triangleglyph_size- 符号的大小,单位为pcolor散点图符号颜色,柱状图外部线的颜色stroke_color- 对于散点图,符号外部是否也要颜色stroke_thickness- 对于散点图,符号外部线的厚度fill_color:柱状图填充色
调整后的参数为
- ...
- <plots>
- <plot>
- type = heatmap
- file = genes_num.txt
- color = blues-9-seq
- r1 = 0.70r
- r0 = 0.61r
- </plot>
- <plot>
- type = scatter
- fill_color = black # 填充色
- stroke_color = black
- glyph = circle
- glyph_size = 5 # 元素大小
- file = genes_num.txt
- r1 = 0.80r
- r0 = 0.71r
- </plot>
- <plot>
- type = histogram
- file = genes_num.txt
- fill_color = blue # 填充色
- r1 = 0.89r
- r0 = 0.81r
- </plot>
- </plots>
- ...
图形效果如下
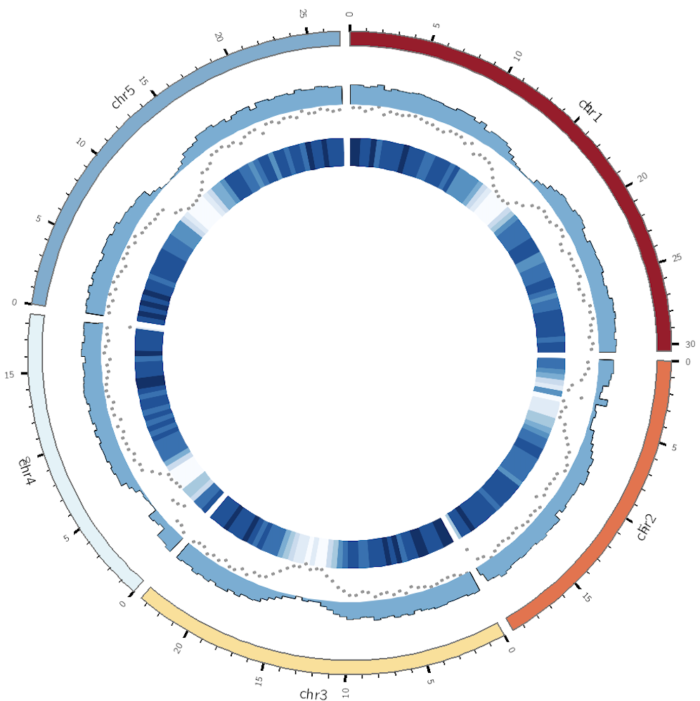
这个效果我个人还是比较满意的。更加复杂的设置,目前还不适合我,需要一步一步来。


