GPT-3,BERT,XLNet这些都是当前自然语言处理(NLP)的新技术,它们都使用一种称为 transformer 的特殊架构组件,这是因为,transformer 这种新机制非常强大,完整的transformer 通常包含三个结构:
- scaled dot-product attention
- self-attention
- cross-attention
- multi-head attention
- positional encoding
让我们从Scaled Dot-Product Attention开始,因为我们还需要它来构建 Multi-Head Attention。
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
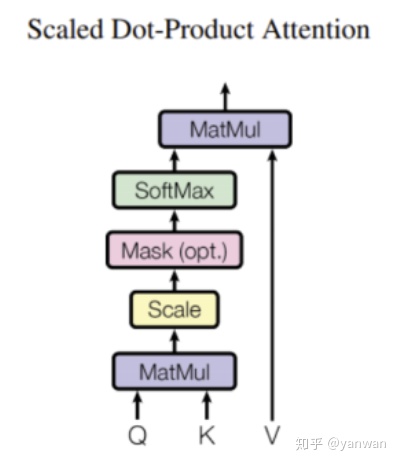
在数学上,Scaled Dot-Product Attention表示为:
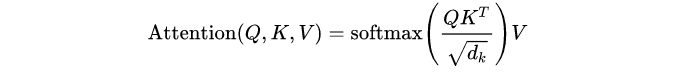
Q,K和V是经过卷积后得到的特征,其形状为(batch_size,seq_length,num_features)。
将查询(Q)和键(K)相乘会得到(batch_size,seq_length,seq_length)特征,这大致告诉我们序列中每个元素的重要性,确定我们“注意”哪些元素。 注意数组使用softmax标准化,因此所有权重之和为1。 最后,注意力将通过矩阵乘法应用于值(V)数组。
scaled dot-product attention 的代码 非常简单-只需几个矩阵乘法,再加上softmax函数。 为了更加简单,我们省略了可选的Mask操作。
- from torch import Tensor
- import torch.nn.functional as f
- def scaled_dot_product_attention(query: Tensor, key: Tensor, value: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- temp = query.bmm(key.transpose(1, 2))
- scale = query.size(-1) ** 0.5
- softmax = f.softmax(temp / scale, dim=-1)
- return softmax.bmm(value)
请注意,MatMul操作在PyTorch中对应为torch.bmm。 这是因为Q,K和V(查询,键和值数组)都是矩阵,每个矩阵的形状均为(batch_size,sequence_length,num_features),矩阵乘法仅在最后两个维度上执行。
在了解了Scaled Dot-Product Attention之后,就很容易理解self-attention和cross-attention了,区别仅仅是Q,K和V的来源不同。
- self-attention的Q,K和V都是同一个输入, 即当前序列由上一层输出的高维表达。
- cross-attention的Q代表当前序列;而K和V是同一个输入,对应的是encoder最后一层的输出结果
Multi-Head Attention
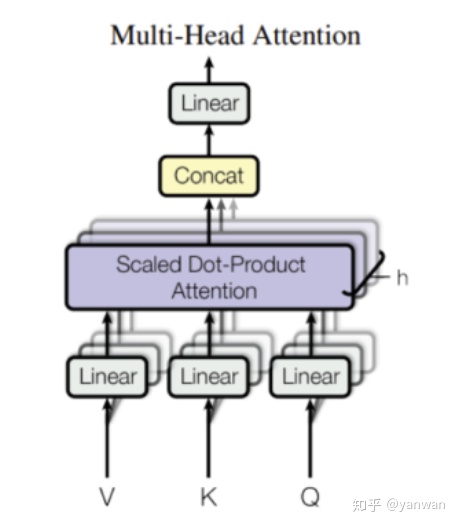
从上图可以看出, Multi-Head Attention 由几个相同的Head Attention组成。 每个关注头包含3个线性层,
![]()
代码如下:
- import torch
- from torch import nn
- class HeadAttention(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, dim_in: int, dim_k: int, dim_v: int):
- super().__init__()
- self.q = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_k)
- self.k = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_k)
- self.v = nn.Linear(dim_in, dim_v)
- def forward(self, query: Tensor, key: Tensor, value: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- return scaled_dot_product_attention(self.q(query), self.k(key), self.v(value))
现在,建立Multi-Head Attention 就非常容易。 只需将num_heads个不同的关注头和一个Linear层组合在一起即可输出。
- class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, num_heads: int, dim_in: int, dim_k: int, dim_v: int):
- super().__init__()
- self.heads = nn.ModuleList(
- [HeadAttention(dim_in, dim_k, dim_v) for _ in range(num_heads)]
- )
- self.linear = nn.Linear(num_heads * dim_v, dim_in)
- def forward(self, query: Tensor, key: Tensor, value: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- return self.linear(
- torch.cat([h(query, key, value) for h in self.heads], dim=-1)
- )
Positional Encoding
在构建完整的transformer之前,我们还需要一个组件:Positional Encoding。 请注意,MultiHeadAttention没有在序列维度上运行, 一切都在特征维上进行,因此它与序列长度无关。 我们必须向模型提供位置信息,以便它知道输入序列中数据点的相对位置。
transformer 论文里使用三角函数对位置信息进行编码:
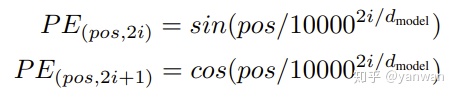
为什么使用正弦编码呢? 因为正弦/余弦函数是周期性的,并且它们覆盖[0,1]的范围。所以,尽管事实证明学习的嵌入表现出同样良好的效果,但作者仍然选择使用正弦编码。
我们只需几行代码即可实现:
- def position_encoding(
- seq_len: int, dim_model: int, device: torch.device = torch.device("cpu"),
- ) -> Tensor:
- pos = torch.arange(seq_len, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(1, -1, 1)
- dim = torch.arange(dim_model, dtype=torch.float, device=device).reshape(1, 1, -1)
- phase = (pos / 1e4) ** (dim // dim_model)
- return torch.where(dim.long() % 2 == 0, -torch.sin(phase), torch.cos(phase))
Transformer
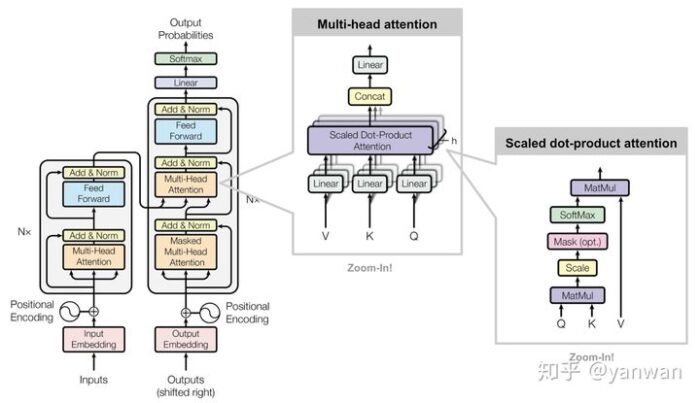
最后,我们准备构建“Transformer”了! 让我们再看一下完整的网络图:
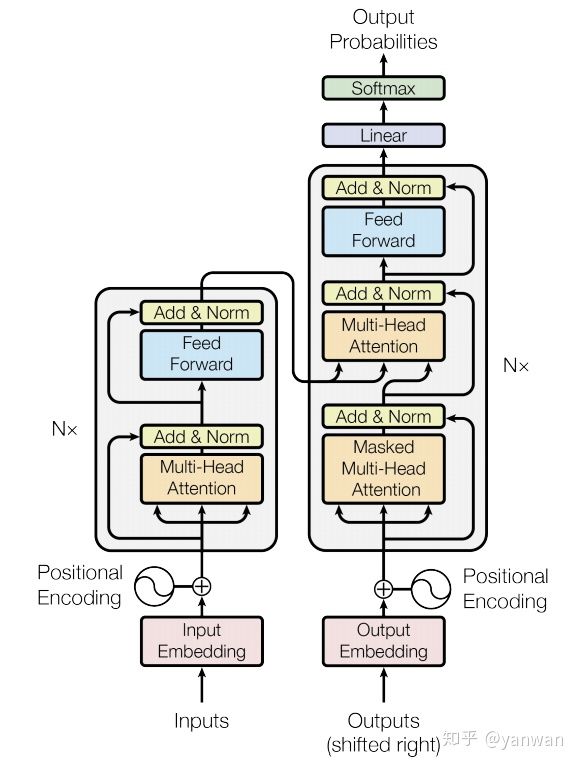
注意,transformer使用编码器-解码器体系结构。 编码器(左)处理输入序列并返回特征向量(或存储向量)。 解码器处理目标序列,并合并来自编码器存储器的信息。 解码器的输出是我们模型的预测!
我们可以彼此独立地对编码器/解码器模块进行编码,然后最后将它们组合。 首先,我们先构建encoder。如下:
- def feed_forward(dim_input: int = 512, dim_feedforward: int = 2048) -> nn.Module:
- return nn.Sequential(
- nn.Linear(dim_input, dim_feedforward),
- nn.ReLU(),
- nn.Linear(dim_feedforward, dim_input),
- )
- class Residual(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, sublayer: nn.Module, dimension: int, dropout: float = 0.1):
- super().__init__()
- self.sublayer = sublayer
- self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(dimension)
- self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
- def forward(self, *tensors: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- # Assume that the "value" tensor is given last, so we can compute the
- # residual. This matches the signature of 'MultiHeadAttention'.
- return self.norm(tensors[-1] self.dropout(self.sublayer(*tensors)))
- class TransformerEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- dim_model: int = 512,
- num_heads: int = 6,
- dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
- dropout: float = 0.1,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- dim_k = dim_v = dim_model // num_heads
- self.attention = Residual(
- MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, dim_model, dim_k, dim_v),
- dimension=dim_model,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- self.feed_forward = Residual(
- feed_forward(dim_model, dim_feedforward),
- dimension=dim_model,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- def forward(self, src: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- src = self.attention(src, src, src)
- return self.feed_forward(src)
- class TransformerEncoder(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- num_layers: int = 6,
- dim_model: int = 512,
- num_heads: int = 8,
- dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
- dropout: float = 0.1,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.layers = nn.ModuleList([
- TransformerEncoderLayer(dim_model, num_heads, dim_feedforward, dropout)
- for _ in range(num_layers)
- ])
- def forward(self, src: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- seq_len, dimension = src.size(1), src.size(2)
- src = position_encoding(seq_len, dimension)
- for layer in self.layers:
- src = layer(src)
- return src
解码器模块非常相似。只是一些小的区别:
- 解码器接受两个参数(target和memory),而不是一个;
- 每层有两个多头部注意力模块,而不是一个;
- 第二个多头注意力接受两个输入的记忆;
- 解码器中包含了self-attention和cross-attention。
- class TransformerDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- dim_model: int = 512,
- num_heads: int = 6,
- dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
- dropout: float = 0.1,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- dim_k = dim_v = dim_model // num_heads
- self.attention_1 = Residual(
- MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, dim_model, dim_k, dim_v),
- dimension=dim_model,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- self.attention_2 = Residual(
- MultiHeadAttention(num_heads, dim_model, dim_k, dim_v),
- dimension=dim_model,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- self.feed_forward = Residual(
- feed_forward(dim_model, dim_feedforward),
- dimension=dim_model,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- def forward(self, tgt: Tensor, memory: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- tgt = self.attention_1(tgt, tgt, tgt)
- tgt = self.attention_2(memory, memory, tgt)
- return self.feed_forward(tgt)
- class TransformerDecoder(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- num_layers: int = 6,
- dim_model: int = 512,
- num_heads: int = 8,
- dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
- dropout: float = 0.1,
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.layers = nn.ModuleList([
- TransformerDecoderLayer(dim_model, num_heads, dim_feedforward, dropout)
- for _ in range(num_layers)
- ])
- self.linear = nn.Linear(dim_model, dim_model)
- def forward(self, tgt: Tensor, memory: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- seq_len, dimension = tgt.size(1), tgt.size(2)
- tgt = position_encoding(seq_len, dimension)
- for layer in self.layers:
- tgt = layer(tgt, memory)
- return torch.softmax(self.linear(tgt), dim=-1)
最后,我们需要将所有内容打包成一个Transformer类,只要把一个编码器和解码器放在一起,然后以正确的顺序通过它们传递数据。
- class Transformer(nn.Module):
- def __init__(
- self,
- num_encoder_layers: int = 6,
- num_decoder_layers: int = 6,
- dim_model: int = 512,
- num_heads: int = 6,
- dim_feedforward: int = 2048,
- dropout: float = 0.1,
- activation: nn.Module = nn.ReLU(),
- ):
- super().__init__()
- self.encoder = TransformerEncoder(
- num_layers=num_encoder_layers,
- dim_model=dim_model,
- num_heads=num_heads,
- dim_feedforward=dim_feedforward,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- self.decoder = TransformerDecoder(
- num_layers=num_decoder_layers,
- dim_model=dim_model,
- num_heads=num_heads,
- dim_feedforward=dim_feedforward,
- dropout=dropout,
- )
- def forward(self, src: Tensor, tgt: Tensor) -> Tensor:
- return self.decoder(tgt, self.encoder(src))
让我们创建一个简单的测试,作为实现的健全性检查。我们可以构造src和tgt的随机张量,检查我们的模型执行没有错误,并确认输出张量具有正确的形状。
- src = torch.rand(64, 16, 512)
- tgt = torch.rand(64, 16, 512)
- out = Transformer()(src, tgt)
- print(out.shape)
- # torch.Size([64, 16, 512])
Conclusions
希望这篇有助于了解transformer是如何搭建的,以及它们是如何工作的。计算机视觉领域,以前可能没有遇到过这些模型,但DETR和ViT已经取得了突破性的成果,预计在未来几年里会看到更多这样的模型。


