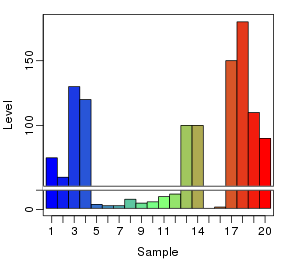
R作图包plotrix提供了不连续y轴(或者称断裂y轴)图形的绘制,原barplot函数的beside参数都不能用,图形也不怎么如意:
- library(plotrix)
- par(mar=c(3,3,1,1))
- par(mgp=c(2,0.5,0))
- y1 <- c(75, 130, 4, 3, 5, 10, 100, 1, 150, 110)
- y2 <- c(60, 120, 3, 8, 6, 12, 100, 2, 180, 90)
- plotrix::gap.barplot(rbind(y1,y2), gap=c(15,50), beside=TRUE, ylab="Level", xlab="Sample")
- ## Warning: "beside" is not a graphical parameter
- ## Warning: "beside" is not a graphical parameter
- ## Warning: "beside" is not a graphical parameter
- ## Warning: "beside" is not a graphical parameter
- ## Warning: "beside" is not a graphical parameter
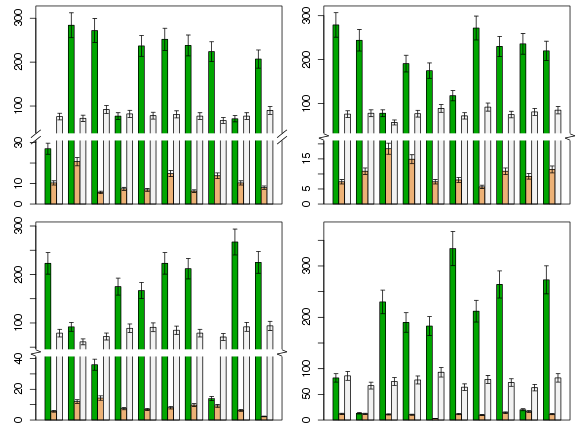
下面是使用自编函数gap.barplot(代码在后面)绘制的图形。函数可以手动设置断点,也可以由函数自动计算。断点位置的符号表示提供了平行线和zigzag两种,并且可设置背景颜色、大小、线型、平行线旋转角度等。参数使用方法请参看函数说明。
- datax <- na.omit(airquality)[,1:4]
- cols <- terrain.colors(ncol(datax) - 1)
- layout(matrix(1:4, ncol=2))
- set.seed(0)
- for (ndx in 1:4){
- dt <- datax[sample(rownames(datax), 10), ]
- dt <- cbind(dt, dt[, -1]* 0.1)
- par(mar=c(1, 3, 0.5, 0.5))
- brkt <- sample(c('normal', 'zigzag'), 1)
- gap.barplot(dt, y.cols=2:4, sd.cols=5:7, col=cols, brk.type=brkt, max.fold=5, ratio=2, cex.error=0.3)
- }
- #' 使用R基本绘图函数绘制y轴不连续的柱形图
- #'
- #' 绘制y轴不连续的柱形图,具有误差线添加功能。断点位置通过btm和top参数设置,如果不设置,函数可自动计算合适的断点位置。
- #' @title gap.barplot function
- #' @param df 长格式的data.frame,即数据框中每一列为一组绘图数据。
- #' @param y.cols 用做柱形图y值的数据列(序号或名称),一列为一组。
- #' @param sd.cols 与y值列顺序对应的误差值的数据列(序号或名称)。
- #' @param btm 低位断点。如果btm和top均不设置,程序将自动计算和设置断点位置。
- #' @param top 高位断点。
- #' @param min.range 自动计算断点的阈值:最大值与最小值的最小比值
- #' @param max.fold 自动计算断点时最大值与下方数据最大值的最大倍数比
- #' @param ratio 断裂后上部与下部y轴长度的比例。
- #' @param gap.width y轴断裂位置的相对物理宽度(非坐标轴实际刻度)
- #' @param brk.type 断点类型,可设为normal或zigzag
- #' @param brk.bg 断点处的背景颜色
- #' @param brk.srt 断点标记线旋转角度
- #' @param brk.size 断点标记线的大小(长度)
- #' @param brk.col 断点标记线的颜色
- #' @param brk.lwd 断点标记线的线宽
- #' @param cex.error 误差线相对长度,默认为1
- #' @param ... 其他传递给R基本绘图函数barplot的参数
- #' @return 返回barplot的原始返回值,即柱形图的x坐标
- #' @examples
- #' datax <- na.omit(airquality)[,1:4]
- #' cols <- cm.colors(ncol(datax))
- #' layout(matrix(1:6, ncol=2))
- #' set.seed(0)
- #' for (ndx in 1:6){
- #' dt <- datax[sample(rownames(datax), 10), ]
- #' par(mar=c(0.5,2,0.5,0.5))
- #' brkt <- sample(c('normal', 'zigzag'), 1)
- #' gap.barplot(dt, col=cols, brk.type=brkt, max.fold=5, ratio=2)
- #' }
- #' @author ZG Zhao
- #' @export
- gap.barplot <- function(df, y.cols=1:ncol(df), sd.cols=NULL, btm=NULL, top=NULL, min.range=10, max.fold=5, ratio=1, gap.width=1,
- brk.type='normal', brk.bg='white', brk.srt=135, brk.size=1, brk.col='black', brk.lwd=1, cex.error=1, ...){
- if (missing(df)) stop('No data provided.')
- if (is.numeric(y.cols)) ycol <- y.cols else ycol <- colnames(df)==y.cols
- if (!is.null(sd.cols))
- if (is.numeric(sd.cols)) scol <- sd.cols else scol <- colnames(df)==sd.cols
- ## Arrange data
- opts <- options()
- options(warn=-1)
- y <- t(df[, ycol])
- colnames(y) <- NULL
- if(missing(sd.cols)) sdx <- 0 else sdx <- t(df[, scol])
- sdu <- y + sdx
- sdd <- y - sdx
- ylim <- c(0, max(sdu) * 1.05)
- ## 如果没有设置btm或top,自动计算
- if (is.null(btm) | is.null(top)){
- autox <- .auto.breaks(dt=sdu, min.range=min.range, max.fold=max.fold)
- if (autox$flag){
- btm <- autox$btm
- top <- autox$top
- } else {
- xx <- barplot(y, beside=TRUE, ylim=ylim, ...)
- if (!missing(sd.cols)) errorbar(xx, y, sdu - y, horiz=FALSE, cex=cex.error)
- box()
- return(invisible(xx))
- }
- }
- ## Set up virtual y limits
- halflen <- btm - ylim[1]
- xlen <- halflen * 0.1 * gap.width
- v_tps1 <- btm + xlen # virtual top positions
- v_tps2 <- v_tps1 + halflen * ratio
- v_ylim <- c(ylim[1], v_tps2)
- r_tps1 <- top # real top positions
- r_tps2 <- ylim[2]
- ## Rescale data
- lmx <- summary(lm(c(v_tps1, v_tps2)~c(r_tps1, r_tps2)))
- lmx <- lmx$coefficients
- sel1 <- y > top
- sel2 <- y >=btm & y <=top
- y[sel1] <- y[sel1] * lmx[2] + lmx[1]
- y[sel2] <- btm + xlen/2
- sel1 <- sdd > top
- sel2 <- sdd >=btm & sdd <=top
- sdd[sel1] <- sdd[sel1] * lmx[2] + lmx[1]
- sdd[sel2] <- btm + xlen/2
- sel1 <- sdu > top
- sel2 <- sdu >=btm & sdu <=top
- sdu[sel1] <- sdu[sel1] * lmx[2] + lmx[1]
- sdu[sel2] <- btm + xlen/2
- ## bar plot
- xx <- barplot(y, beside=TRUE, ylim=v_ylim, axes = FALSE, names.arg=NULL, ...)
- ## error bars
- if(!missing(sd.cols)) errorbar(xx, y, sdu - y, horiz=FALSE, cex=cex.error)
- ## Real ticks and labels
- brks1 <- pretty(seq(0, btm, length=10), n=4)
- brks1 <- brks1[brks1 >= 0 & brks1 < btm]
- brks2 <- pretty(seq(top, r_tps2, length=10), n=4)
- brks2 <- brks2[brks2 > top & brks2 <= r_tps2]
- labx <- c(brks1, brks2)
- ## Virtual ticks
- brks <- c(brks1, brks2 * lmx[2] + lmx[1])
- axis(2, at=brks, labels=labx)
- box()
- ## break marks
- pos <- par("usr")
- xyratio <- (pos[2] - pos[1])/(pos[4] - pos[3])
- xlen <- (pos[2] - pos[1])/50 * brk.size
- px1 <- pos[1] - xlen
- px2 <- pos[1] + xlen
- px3 <- pos[2] - xlen
- px4 <- pos[2] + xlen
- py1 <- btm
- py2 <- v_tps1
- rect(px1, py1, px4, py2, col=brk.bg, xpd=TRUE, border=brk.bg)
- x1 <- c(px1, px1, px3, px3)
- x2 <- c(px2, px2, px4, px4)
- y1 <- c(py1, py2, py1, py2)
- y2 <- c(py1, py2, py1, py2)
- px <- .xy.adjust(x1, x2, y1, y2, xlen, xyratio, angle=brk.srt*pi/90)
- if (brk.type=='zigzag'){
- x1 <- c(x1, px1, px3)
- x2 <- c(x2, px2, px4)
- if (brk.srt > 90){
- y1 <- c(y1, py2, py2)
- y2 <- c(y2, py1, py1)
- } else {
- y1 <- c(y1, py1, py1)
- y2 <- c(y2, py2, py2)
- }
- }
- if (brk.type=='zigzag') {
- px$x1 <- c(pos[1], px2, px1, pos[2], px4, px3)
- px$x2 <- c(px2, px1, pos[1], px4, px3, pos[2])
- mm <- (v_tps1 - btm)/3
- px$y1 <- rep(c(v_tps1, v_tps1 - mm, v_tps1 - 2 * mm), 2)
- px$y2 <- rep(c(v_tps1 - mm, v_tps1 - 2 * mm, btm), 2)
- }
- par(xpd=TRUE)
- segments(px$x1, px$y1, px$x2, px$y2, lty=1, col=brk.col, lwd=brk.lwd)
- options(opts)
- par(xpd=FALSE)
- invisible(xx)
- }
- ## 绘制误差线的函数
- errorbar <- function(x, y, sd.lwr, sd.upr, horiz=FALSE, cex=1, ...)
- {
- if(missing(sd.lwr) & missing(sd.upr)) return(NULL)
- if(missing(sd.upr)) sd.upr <- sd.lwr
- if(missing(sd.lwr)) sd.lwr <- sd.upr
- if(!horiz){
- arrows(x, y, y1=y-sd.lwr, length=0.1*cex, angle=90, ...)
- arrows(x, y, y1=y+sd.upr, length=0.1*cex, angle=90, ...)
- } else{
- arrows(y, x, x1=y-sd.lwr, length=0.1*cex, angle=90, ...)
- arrows(y, x, x1=y+sd.upr, length=0.1*cex, angle=90, ...)
- }
- }
- .xy.adjust <- function(x1, x2, y1, y2, xlen, xyratio, angle){
- xx1 <- x1 - xlen * cos(angle)
- yy1 <- y1 + xlen * sin(angle)/xyratio
- xx2 <- x2 + xlen * cos(angle)
- yy2 <- y2 - xlen * sin(angle)/xyratio
- return(list(x1=xx1, x2=xx2, y1=yy1, y2=yy2))
- }
- ## 自动计算断点位置的函数
- .auto.breaks <- function(dt, min.range, max.fold){
- datax <- sort(as.vector(dt))
- flags <- FALSE
- btm <- top <- NULL
- if (max(datax)/min(datax) < min.range) return(list(flag=flags, btm=btm, top=top))
- m <- max(datax)
- btm <- datax[2]
- i <- 3
- while(m/datax[i] > max.fold){
- btm <- datax[i]
- flags <- TRUE
- i <- i + 1
- }
- if (flags) {
- btm <- btm + 0.05 * btm
- x <- 2
- top <- datax[i] * (x - 1)/x
- while (top < btm) {
- x <- x + 1
- top <- datax[i] * (x - 1)/x
- if (x > 100) {
- flags <- FALSE
- break
- }
- }
- }
- return(list(flag=flags, btm=btm, top=top))
- }
原文来自:http://blog.csdn.net/u014801157/article/details/24372371



1F
这个函数怎么可以加横坐标各组名称
来自外部的引用